Transport of energy and mass is fundamental to many
biological and environmental processes. Areas, from food processing to thermal
design of building to biomedical devices to pollution control and global
warming, require knowledge of how energy and mass can be transported through
materials (mass, momentum, heat transfer).
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bioprocess |
|
|
|
|
|
|
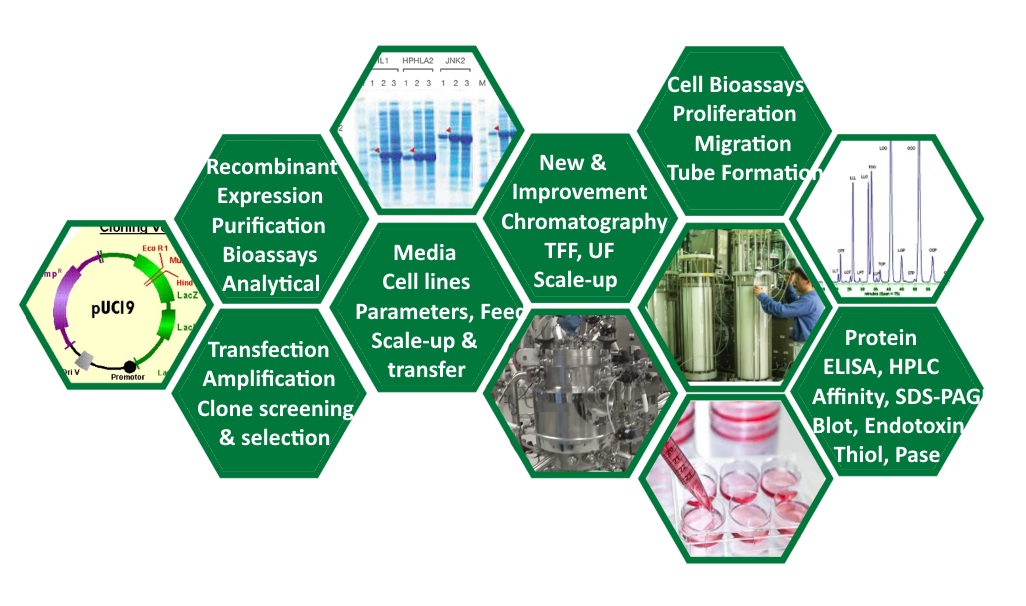
Upstream bioprocessing
Therapeutic cell
manufacturing processes can be separated into upstream processes and downstream
processes. The upstream process is defined as the entire process from early cell isolation
and cultivation, to cell banking and culture expansion of the cells until final
harvest (termination of the culture and collection of the live cell batch).
Aside from technology challenges, concerning the scalability
of culture apparatus, a number of raw material supply risks have emerged in
recent years[when?], including the availability of GMP grade fetal bovine
serum[citation
needed].
The upstream part of a bioprocess refers to the first step in which
microbes/cells are grown, e.g. bacterial or mammalian cell lines (see cell culture), in bioreactors.
|

|
Upstream processing involves all
the steps related to inoculum development, media development, improvement of
inoculum by genetic engineering process, optimization of growth kinetics so that
product development can improve tremendously. Fermentation has two parts:
upstream and downstream. After product development, the next step is the
purification of product for desired quality. When they reach the desired density
(for batch and fed-batch cultures) they are harvested and moved to the
downstream section of the bioprocess. |
|
|
Downstream bioprocessing
The downstream part of a bioprocess refers to the part where the cell mass from
the upstream are processed to meet purity and quality requirements. Downstream
processing is usually divided into three main sections: cell disruption, a
purification section and a polishing section. The volatile products can be
separated by distillation of the harvested culture without pre-treatment.
Distillation is done at reduced pressure at continuous stills. At reduced
pressure distillation of product directly from fermentor may be possible. The
steps of downstream processing are: |

|
- Separation of biomass: separating the biomass
(microbial cells) generally carried out by centrifugation or
ultra-centrifugation. If the product is biomass, then it is recovered for
processing and spent medium is discarded. If the product is extra cellular the
biomass will be discarded. Ultra filtration is an alternative to the
centrifugation.
- Cell disruption: If the desired product is intra
cellular the cell biomass can be disrupted so that the product should be
released. The solid-liquid is separated by centrifugation or filtration and cell
debris is discarded.
- Concentration of broth: The spent medium is
concentrated if the product is extracellular.
- Initial purification of metabolites: According to
the physico-chemical nature of the product molecule several methods for recovery
of product from the clarified fermented broth were used (precipitation, etc.)
- De-watering: If low amount of product is found in
very large volume of spent medium, the volume is reduced by removing water to
concentrate the product. It is done by vacuum drying or reverse osmosis.
- Polishing of metabolites: this is the final step
of making the product 98 to 100% pure. The purified product is mixed with
several inert ingredients called excipients. The formulated product is packed and sent
to the market for the consumers.
|
|
|
Based on our very high quality and innovative environments both in public and
private domains in our Biotechnology & Pharmaceutical Community,
http://www.chromnet.net/Bio-Community.aspx
We have key professional core technology, abundant practical experiences,
extensive resources and integrated capabilities for Bioprocess Services. Our
prominent team partners, including the
Blue Blood Biotech, have
built Gene recombinant, Recombinant protein expression, Protein
Purification, and Analytical Methods Development core technologies, providing
efficient service capabilities including Protein Engineering, Protein Expression
Development, Recovery & Purification Development, Cell-based Bioassays,
Analytical Methods Development, etc.
|
|
|
|
Core Technology |
|
|
|
|
|
Gene recombinant technology |
Polymerase chain reaction
DNA electrophoresis
Stable clone screening and selection |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Recombinant protein expression |
Yeast expression system
Mammalian expression system |
|
|
|
|
|
Protein Purification |
Lab scale system
Pilot scale system
Production scale system |
|
|



|
|
|
|
Analytical Methods Development
|
ELISA assays
HPLC-IEX, SEC, RP columns
SDS-PAGE analysis |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cell-based potency assays |
Cell proliferation
Cell migration
‧ Boyden chamber migration
‧ Transwell migration
‧ FluoroBlok migration
‧ Scratch migration
Tube formation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
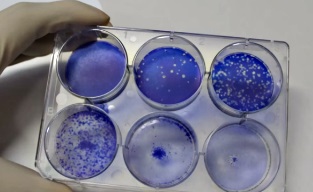
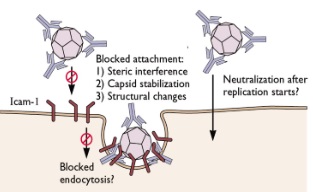
Virus cultivation |
Plaque assay
Neutralization assay |
|

|
|
|
|
Bioprocess Services |
1.Protein Engineering
2.Protein Expression Development
3.Recovery & Purification Development
4.Cell-based Bioassays
5.Analytical Methods Development |
|
|
|
Protein Engineering |
We can take cell line to develop your project from DNA to clone screening and
selection . We have experience working with different types of expression system
Ex. Pichia pastoris, CHO, .....
Our service includes :
-Transfection
-Amplification
-Clone screening
-Clone selection |
|
|
|
|
|
Protein Expression Development |
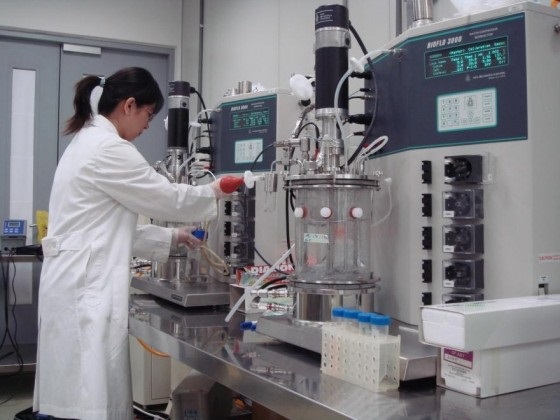
We provide the upstream culture process development and runs batch bioreactor
systems with different type of expression system. We can develop process through
a combination of screening, media screening , yield analysis, and systematic
optimization of parameters. Key equipment includes 5L New BrunSwick Scientific
bioreactors with mass flow controllers for gas mixing, continuous centrifuge,
BelloStage-3000, CO2 incubator and Laminar flow. |
Service includes :
-Cell propagation in flasks, BelloStage-3000, and Bioreactors
-Clone selection based on productivity/stability
-Media screening/optimization
-Adaptation of cell lines
-Bioreactor parameter optimization
-Development of feed strategies
-Process scale-up Scale-up/Technology transfer
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
Recovery & Purification Development |
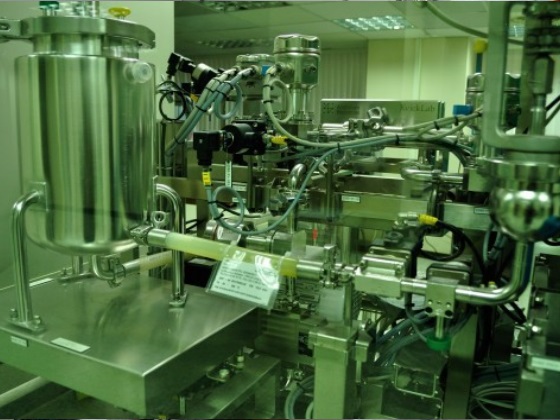
Our purification development laboratory is equipped to develop new purification
processes, improve and trouble-shoot unit operation of purification process, and
systematically evaluate process parameters to improve overall process economics.
Key process equipment includes a AKTA purifier10, AKTA Primeplus and fraction
collector, AKTA Piolt、Bioprocess system、Lab TFF system、XK &BPG Column、 UniFlux
10A &30A. |
Service includes :
-Develop new recovery/purification processes
-Improve and trouble-shoot existing unit operations
-Column chromatography
-- affinity, HIC, IEX, SEC -TFF, Ultrafiltration
-Scale-up/Technology transfer
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
Cell-based Bioassays |
Cells were purchased from Bioresource Collection and Research Center (BCRC) and
American Type Culture Collection (ATCC).
Key equipment includes Pressurized Clean Room, Optima/NIKON microscopies with
digital camera, Laminar flow, CO2 incubator, Fluorescent activity assays |
Service includes :
-Cell Proliferation
-Cell Migration
-Boyden chamber
-Transwell
-FluoroBlok
-Scratch wound healing
-Tube Formation |

|
|
|
|
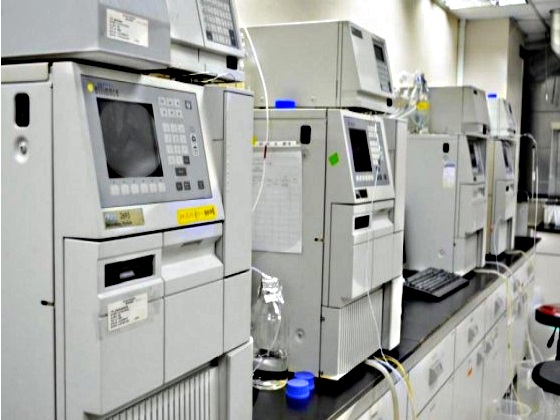
Analytical Methods Development |
Services and methods include testing for product/process related impurities
anddeveloping release and in-process assays in support of microbial
fermentation,cell culture and purification development. |
Service includes :
-BCA /Bradford protein assays
-A280 protein determination
-pH
-Conductivity
-ELISA assays
-HPLC-affinity, IEX, HIC, SEC, RP-HPLC
-SDS-PAGE analysis
-IEF analysis
-Western blot analysis
-LAL Endotoxin assays
-Free-thiol assay
-Protease activity assay
-Cellulase activity assay |

|
|
|